Health
FODMAP 101: A Detailed Beginner’s Guide
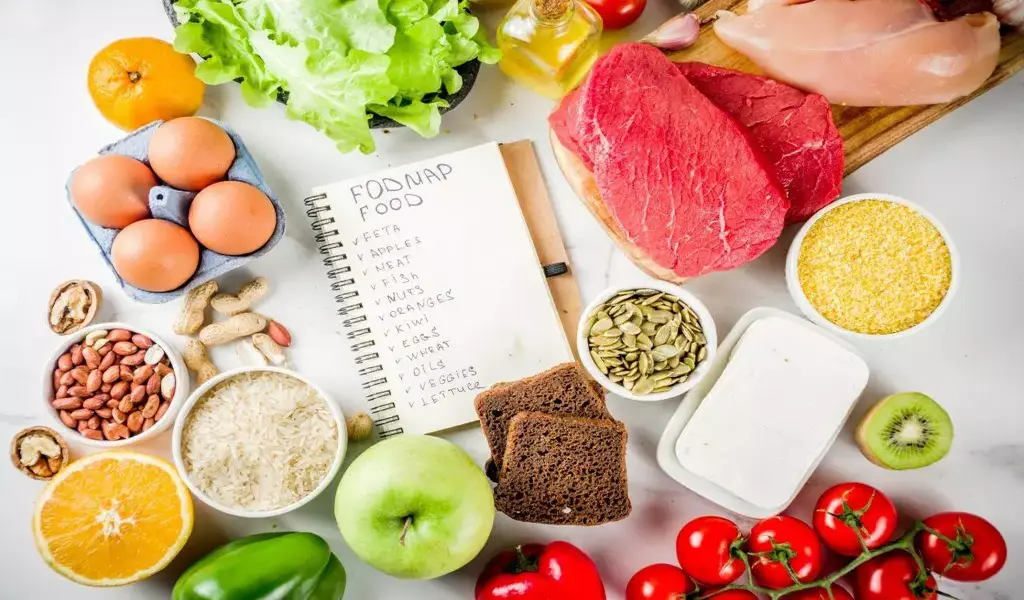

FODMAP entails a group of short-chain carbohydrates found in many common foods. These include Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols. When these short-chain carbohydrates aren’t fully absorbed in the small intestine, they travel to the large intestine, where gut bacteria ferment them.
This process can produce methane and carbon dioxide gas, which can cause abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence, and diarrhea.
The FODMAP diet is a low-FODMAP diet used to help manage symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other gut disorders. While a FODMAP diet can be helpful for some people, it’s not suitable for everyone. Working with a Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN) or other healthcare providers is vital before making any significant changes to your diet.
How does it work?
The FODMAP diet is a temporary elimination diet that removes high-FODMAP foods from your diet for 6-8 weeks. After the initial elimination phase, you’ll slowly reintroduce foods to see how they affect your symptoms.
This process can help you identify which foods trigger your symptoms and allow you to create a personalized long-term eating plan. It would help if you considered any variable that could affect your test results, such as stress, medications, and other food intolerances.
What are the benefits?
There are various benefits, such as;
1) Relief from IBS symptoms
A low-FODMAP diet is an effective treatment for IBS. In one study, 76% of people with IBS who followed a low-FODMAP diet reported symptom relief.
2) Improved quality of life
IBS can significantly impact your quality of life. Studies have shown that following a low-FODMAP diet can improve your quality of life and reduce IBS-related anxiety and depression.
3) It may help other gut disorders
In addition to IBS, a low-FODMAP diet may also be effective for other gut disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO).
What are the risks?
There are a few risks to be aware of when following a low-FODMAP diet, such as;
1) It’s a restrictive diet
A low-FODMAP diet can be hard to follow because it eliminates many common foods. This can make it challenging to get all the nutrients your body needs.
2) It may not be necessary
Eliminating FODMAPs from your diet may not be necessary if you don’t have IBS or another gut disorder. If you stop FODMAPs unnecessarily, you may miss out on essential nutrients.
3) You may not be able to identify your triggers
A low-FODMAP diet can be challenging to stick to, and you may not be able to identify your food triggers if you don’t see improvement in your symptoms.
4) You may have to trial and error
trigger foods; it can take some time and experimentation to figure out which foods work for you.
5) It’s not a cure
A low-FODMAP diet can help manage your symptoms, but it’s not a cure for IBS or other gut disorders.
Conclusion
A low-FODMAP diet can effectively treat IBS and other gut disorders. However, a restrictive diet may not be necessary for everyone. Working with a Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN) or other healthcare providers is vital before making any significant changes to your diet.
People Also Read:
What Is Listeria? Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, & Prevention
Thailand Postpones Labeling Covid-19 an Endemic Disease
6 Ways Men can Handle Stress to Remain Fit
Nine Foods that Speed up your Metabolism