News
Why Climate Change Is Now an Urgent Global Emergency – Exploring the Science and Solutions

(CTN News) – Climate change, a term that has lingered in the background for decades, has now risen to the forefront of global concerns. Scientists worldwide are increasingly using the term ’emergency’ to describe the situation. This article explores the reasons behind this sense of urgency and the implications for our planet.
The climate is undergoing significant and rapid changes, which have led scientists to categorize the situation as an emergency. This declaration signifies that immediate action is essential to prevent potentially catastrophic consequences. In this article, we will delve into the factors contributing to this shift in terminology and examine the pressing issues linked to climate change.
The Scientific Consensus
Data and Research
The shift towards labeling climate change as an ’emergency’ is grounded in solid scientific research. Over the years, the data collected has revealed alarming trends, such as the continuous rise in global temperatures and the increased frequency of extreme weather events. These trends paint a dire picture of the future.
Data-driven evidence plays a pivotal role in our understanding of climate change. Temperature records, ice core samples, and satellite observations all confirm the same troubling pattern: the Earth is warming at an unprecedented rate. Climate scientists rely on these data sources to predict future trends, and the outlook is concerning. The term ’emergency’ has been adopted to emphasize the severity and urgency of the situation.
Key Findings
Key findings include the fact that the past few decades have seen a significant increase in greenhouse gas emissions, primarily from human activities. This has resulted in a warmer planet, causing polar ice to melt and sea levels to rise, threatening coastal communities. Such findings underscore the urgency of addressing climate change.
Greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to a greenhouse effect that warms the planet. This effect is primarily driven by human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
The consequences are profound, with rising sea levels endangering low-lying coastal regions and impacting billions of people. These findings, supported by rigorous scientific research, drive the message home: immediate action is required to mitigate these effects.
Extreme Weather Events
Rising Temperatures
One of the most visible impacts of climate change is the rise in temperatures. Heatwaves are becoming more frequent and intense, resulting in a higher number of heat-related illnesses and deaths.
Rising temperatures are evident in prolonged and intense heatwaves that affect various regions of the world. These extreme heat events not only cause discomfort but also have dire consequences for human health.
Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and children, are at risk of heat-related illnesses. Additionally, higher temperatures exacerbate issues like drought and water scarcity, affecting agriculture and food production.
Natural Disasters
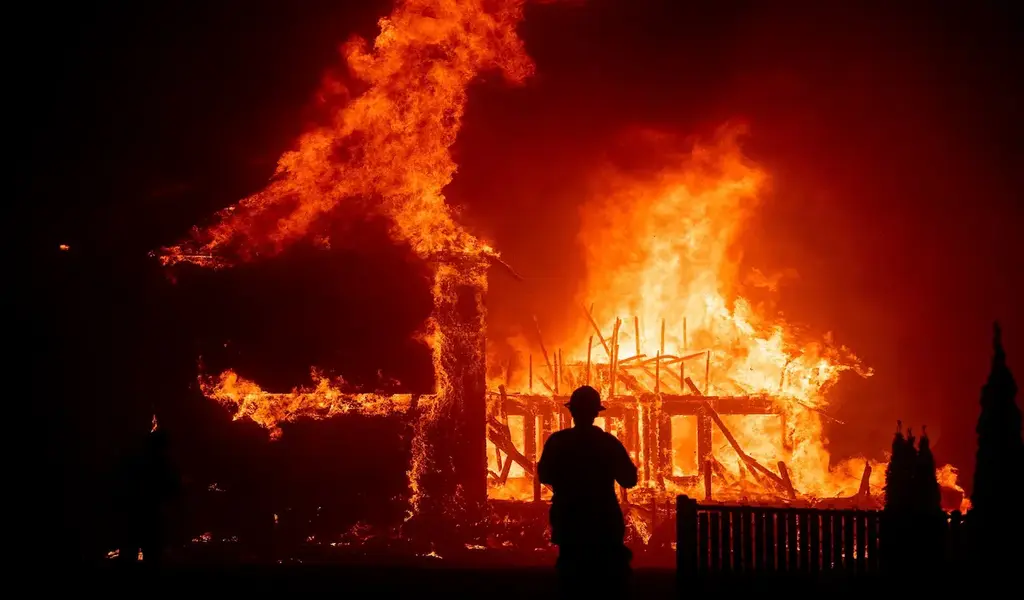
Climate change also fuels natural disasters. Hurricanes, wildfires, and floods have become more destructive and deadly due to the changing climate. This poses a significant threat to human lives and infrastructure.
Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and wildfires, are becoming more frequent and severe. These disasters result in loss of life, destruction of homes, and massive economic costs.
The intensity and frequency of such events are attributed to the warming of the Earth, which is linked to climate change. Scientists emphasize that these occurrences are no longer anomalies but part of a pattern that is escalating, making the ’emergency’ label apt.
Impact on Ecosystems
Biodiversity Loss
The natural world is also suffering. Ecosystems are disrupted, leading to biodiversity loss. Species are disappearing at an alarming rate, affecting the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems.
Biodiversity loss is a critical consequence of climate change. Ecosystems that once thrived are now under threat, resulting in the extinction of numerous species. This disruption has a profound impact on the environment and food chains, ultimately affecting human well-being. Scientists warn that the current rate of biodiversity loss is unsustainable and requires immediate intervention.
Ocean Acidification
The oceans, often called the Earth’s lungs, are absorbing excess carbon dioxide, causing ocean acidification. This disrupts marine life, with ripple effects on the entire food chain.
Ocean acidification is a lesser-known but equally significant consequence of climate change. The excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is absorbed by the oceans, causing them to become more acidic.
This harms marine life, especially creatures with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons, like corals and some types of plankton. These changes in ocean chemistry have a cascading effect throughout the food chain, ultimately impacting human populations that rely on seafood.
Human Health and Well-being
Air Quality
Climate change worsens air quality, increasing the prevalence of respiratory illnesses and making outdoor activities more hazardous.
As temperatures rise, the quality of the air we breathe is compromised. The increased occurrence of heatwaves and altered weather patterns leads to poor air quality, with a higher concentration of air pollutants.
This, in turn, contributes to respiratory illnesses, particularly in urban areas. The association between climate change and deteriorating air quality is clear, making it a pressing health concern.
Disease Spread
Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns create ideal conditions for disease vectors, leading to the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue fever.
Climate change affects the distribution and behavior of disease-carrying vectors, such as mosquitoes. As temperatures rise, these vectors expand their habitats, leading to the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue fever to regions where they were previously uncommon. This poses a significant health risk to communities and requires proactive measures to prevent and control the diseases.
Economic Consequences
Agriculture and Food Security
Crop yields are under threat due to changing weather patterns, affecting food security globally. This can lead to food shortages and price spikes.
Agriculture, a cornerstone of human civilization, is under threat due to unpredictable weather patterns caused by climate change. Crops face challenges like droughts, floods, and new pests that affect yield and quality. As a result, food security becomes an issue, with the potential for food shortages and increased prices, particularly in vulnerable regions.
Insurance Costs
Increased frequency and severity of natural disasters put a massive financial burden on insurance companies, which, in turn, affects the global economy.
The surge in natural disasters has economic consequences. Insurance companies face growing claims due to the destruction caused by hurricanes, wildfires, and floods. As insurance costs rise, this financial burden extends to governments and individuals. The economic impact of climate change is not limited to these costs alone but also includes reduced productivity, property damage, and disruptions to supply chains.
Political Response
International Agreements
The international community has recognized the need to address climate change, resulting in agreements like the Paris Agreement. However, the urgency to meet the goals is increasing.
Global recognition of climate change as an emergency has led to international agreements aimed at curbing emissions and limiting temperature increases. The Paris Agreement, signed by 196 countries, is a landmark accord that commits nations to reducing their greenhouse gas emissions. However, the increasing urgency necessitates even more ambitious actions to meet the agreement’s goals and prevent catastrophic climate outcomes.
Policy Changes
Governments are adopting new policies and regulations to reduce emissions and promote sustainability. These changes aim to slow the progression of climate change.
Many governments are taking steps to address climate change. This includes policies to transition to cleaner energy sources, incentivize electric vehicles, and regulate industry emissions. These changes are vital in the fight against climate change and are an acknowledgment of the ’emergency’ status of the situation.
Technological Solutions
Energy
Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is crucial in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Renewable energy offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, as it produces electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. The widespread adoption of these technologies is essential to slowing down climate change.
The development of renewable energy technologies has reached a point where they are not only environmentally friendly but also economically viable. Solar panels and wind turbines are becoming more affordable and efficient, making them accessible for both individuals and large-scale energy projects.
Carbon Capture
Innovative technologies to capture and store carbon emissions are being developed to counteract the damage already done. Carbon capture involves trapping carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power plants and storing them underground. This technology is a critical tool in reducing the overall carbon footprint and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Challenges and Obstacles
Skepticism and Denial
Despite overwhelming scientific evidence, some still deny the existence of climate change, hindering progress. Climate change denial remains a significant obstacle to collective action. While the scientific consensus is clear, a small but vocal minority continue to deny the reality of climate change. Overcoming skepticism and disinformation is crucial in garnering public and political support for climate action.
Economic Interests
Certain industries resist change due to financial interests tied to fossil fuels. This poses a significant challenge to the global response. Fossil fuel industries, including coal, oil, and natural gas, have powerful economic interests. Transitioning away from these energy sources threatens their profitability. This economic resistance can influence policy decisions and slow down the adoption of clean energy technologies.
The Role of Individuals
Lifestyle Changes
Every individual can contribute by adopting sustainable practices in their daily lives, from reducing waste to conserving energy. Lifestyle changes are within the reach of everyone. Simple actions like reducing, reusing, and recycling can help minimize waste and reduce the carbon footprint. Using public transportation, biking, or carpooling can reduce emissions from personal vehicles. These individual efforts, when multiplied across communities, have a substantial impact on reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Advocacy
People can also support climate action by advocating for change through grassroots efforts and community involvement. Activism and advocacy are powerful tools for driving change. Individuals can join or support organizations dedicated to environmental conservation and climate action. They can also engage with local and national policymakers, voicing their concerns and demanding action on climate change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the urgency of addressing climate change as an ’emergency’ cannot be overstated. The evidence is clear: climate change is real, and its impacts are already being felt globally. It is a global crisis that requires immediate, collective action from individuals, communities, governments, and industries. The adoption of sustainable practices, technological solutions, and policies to reduce emissions is essential to mitigate the effects of climate change and protect the future of our planet.