News
U.N Member Nations Approve Plan To End Tuberculosis Worldwide Within Five Years
(CTN NEWS) – On Friday, member nations of the United Nations unanimously endorsed a “political declaration” aimed at eradicating tuberculosis worldwide within the next five years.
This comprehensive plan, meticulously crafted by the World Health Organization (WHO), received unanimous approval during the high-level meeting on tuberculosis at the U.N. General Assembly in New York.
The plan’s objectives are ambitious, encompassing targets such as providing TB prevention services to 90% of the global population, implementing the WHO-recommended TB rapid test for initial diagnoses, and facilitating the licensing of at least one new TB vaccine by the year 2027.
Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the Director-General of the World Health Organization (WHO) and leader of the meeting, has highlighted that many of the objectives set during the inaugural high-level tuberculosis meeting in 2018 remained unmet, primarily due to the disruptive impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Challenges in Tuberculosis Eradication
Specifically, the goal of providing treatment to 44 million individuals afflicted with TB fell short by approximately 10 million people, while the aim of reaching 30 million individuals with preventive treatment was only achieved halfway.
Additionally, the target of securing $2 billion in funding for TB research saw a shortfall of about half between 2018 and 2020.
Despite being one of the world’s most lethal infectious diseases, causing over a million deaths annually and infecting more than 10 million people, TB continues to pose a substantial global health challenge.
Furthermore, there are approximately 500,000 cases of drug-resistant TB reported each year.
The WHO’s data indicates an increase in new TB cases and deaths between 2020 and 2021, particularly during the peak years of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, concerted efforts since then have shown some improvement in these statistics.
Just as it did for COVID-19 during the pandemic, the WHO has launched a TB vaccine accelerator program. This initiative is designed to expedite the development, testing, and authorization of new TB vaccines.
Currently, only one TB vaccine has received licensing. While it has demonstrated moderate effectiveness in preventing severe TB in infants, it falls short in safeguarding adolescents and adults, who account for 90% of TB transmission on a global scale.
Tuberculosis (TB): Key Insights
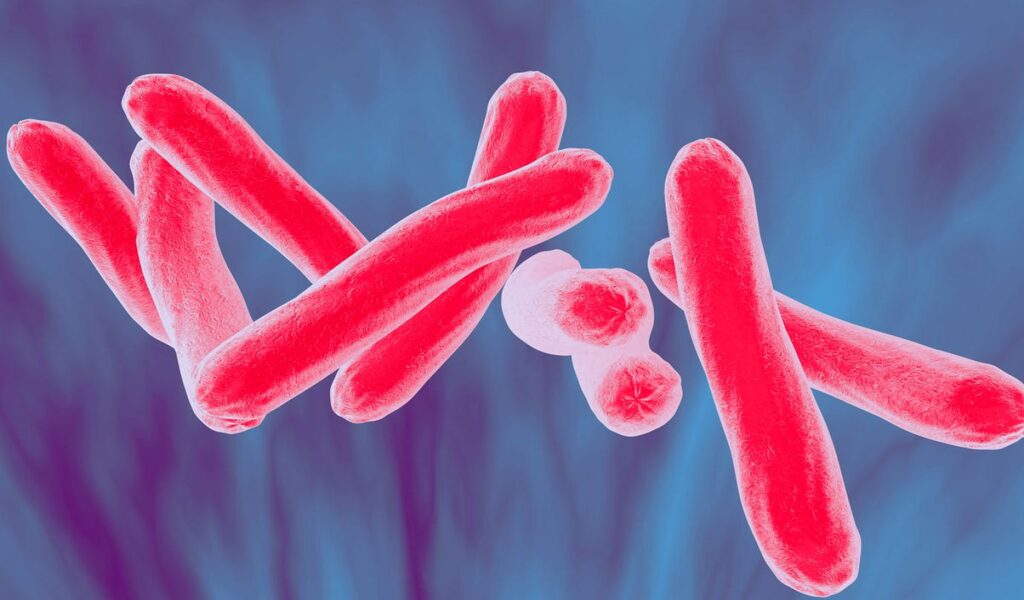
TB stands for tuberculosis, which is a bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. It is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
TB is a contagious disease that spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Here are some key points about tuberculosis (TB):
- Symptoms: Common symptoms of TB include a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss. In more advanced cases, it can cause chest pain and coughing up blood.
- Diagnosis: TB is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical exams, and various tests such as chest X-rays, sputum tests, and blood tests.
- Treatment: TB is treatable with antibiotics, but it usually requires a long course of treatment, often lasting several months. It’s crucial to complete the entire course of antibiotics to prevent drug-resistant strains of TB from developing.
- Prevention: TB can be prevented through measures such as vaccination (using the BCG vaccine in some countries), good hygiene practices, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
- Global Impact: TB remains a significant global health concern, particularly in regions with limited access to healthcare resources. Efforts to control and eliminate TB include screening, diagnosis, and treatment programs.
- Drug-Resistant TB: Drug-resistant strains of TB, such as multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) and extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB), are a growing concern and are more challenging to treat.
- History: Tuberculosis has been a major public health issue for centuries and has had a significant impact on human history and literature, often referred to as “consumption” or “the white plague.”
RELATED CTN NEWS:
Pope Francis Rejects ‘Emergency’ Label For Migration, Advocates For Compassion In Marseille Address
Long-Term Effects Of Severe COVID-19: Study Reveals Significant Organ Impairments
IHC Schedules Imran Khan’s Bail Application Hearing In Missing Cipher Case For Monday