Health
Discovery Of Epidermal Hemoglobin Reveals Skin’s Protective Abilities
(CTN News) – In our understanding of how the skin protects the body, the discovery of hemoglobin in the epidermis represents a defining moment in our understanding of the skin’s protective abilities.
It has been discovered that hemoglobin plays a previously unknown role in the epidermis, our skin’s outermost layer, in addition to its functions in red blood cells and oxygen transport.
Hemoglobin, a protein normally found in red blood cells, has been found for the first time in the epidermis. Taking care of our skin is crucial to protecting us from the outside world, according to a study in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Hemoglobin was detected in the human epidermis and hair follicles due to the researchers’ curiosity to understand how the skin protects the body. We can now gain a deeper understanding of how our skin keeps us safe.
Masayuki Amagai, MD, Ph.D., from the Department of Dermatology at Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, and the Laboratory for Skin Homeostasis at RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences, Yokohama, explains: “In the epidermis, the keratinized stratified squamous epithelium is mtes.
In the course of keratinocyte differentiation and the formation of the outer skin barrier, various genes with protective functions have been identified. These genes regulate the expression of genes.
Due to difficulties obtaining sufficient amounts of terminally differentiated keratinocytes for transcriptome analysis, other barrier-related genes weren’t detected in previous analyses.
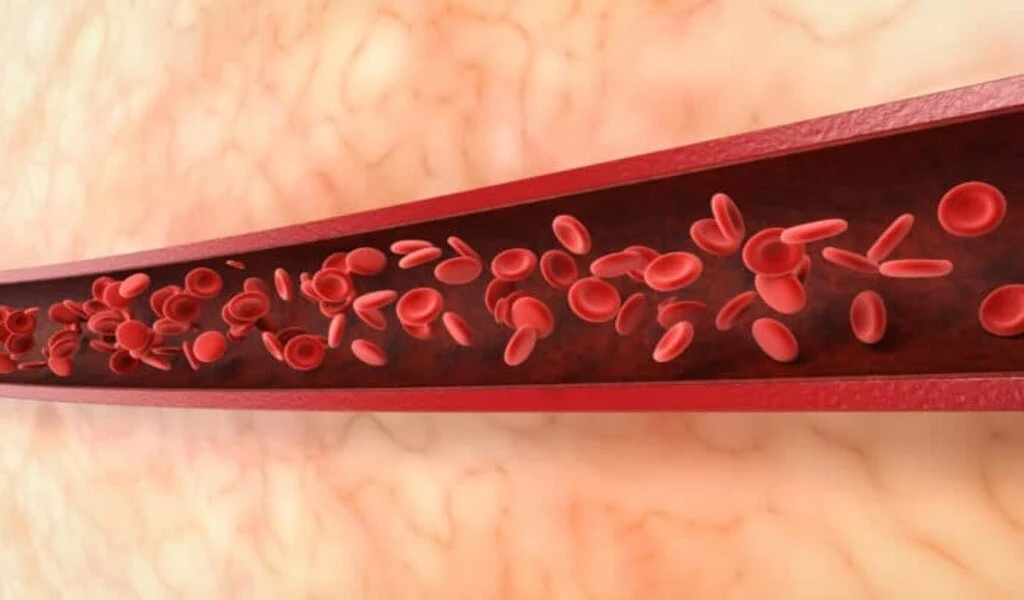
As a matter of fact, the epidermis is the only part of the body that contains hemoglobin, a protein that binds gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitric oxide.
Therefore, it has the potential to function as an antioxidant and to play a role in the barrier function as well. According to Professor Amagai’s research, genes responsible for producing hemoglobin are highly active in the upper epidermis of the body.
The study confirmed the presence of hemoglobin α proteins in keratinocytes using immunostaining, which was used to confirm its presence.
Additionally, the study found that epidermal hemoglobin protects keratinocytes from UV irradiation,
As well as reducing mitochondrial dysfunction, as a result of protecting them against oxidative stress. As a result, we can conclude that hemoglobin expression is a natural defense against aging and cancer of the skin.
Hemoglobin expression by keratinocytes is considered one of the most effective endogenous defense mechanisms against the aging of the skin and the development of skin cancers.
As a result of these findings, we are able to increase our understanding of hemoglobin’s multifaceted function, as well as highlight its potential role in the intricate web of mechanisms that help safeguard our skin from the harmful effects of the environment.
In addition to opening new avenues for research into skincare and dermatology, this discovery offers insights that could eventually lead to innovative approaches for maintaining skin health and preventing skin-related disorders that are related to the skin.
SEE ALSO:
Mosquitoes That Carry Malaria Can Be Controlled By Adding Soap
With An Inexpensive Pill, Kidney Disease-Related Deaths Could Be Reduced
Sanofi, AZ’s Beyfortus’ Supply Shortage Is Eased With Extra Doses By The CDC