News
Beyond THC and CBD: Unveiling Lesser-Known Cannabinoid Potentials

The world of cannabis is not limited to the well-known compounds THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (Cannabidiol). These two cannabinoids have dominated the spotlight due to their prevalence and significant research backing their effects on the human body.
THC is best known for its psychoactive properties, which can alter one’s state of consciousness, while CBD has been widely recognized for its potential therapeutic benefits without the intoxicating effects. However, the cannabis plant synthesizes many more cannabinoids, each with unique properties and potential applications in health and medicine.
Researchers are increasingly interested in rare cannabinoids, such as cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). These compounds are present in much lower concentrations in the plant but are attracting attention for their potential health benefits.
For instance, CBG has been gathering interest for its nonintoxicating effects and potential to alleviate conditions like anxiety, pain, and inflammation. Investigations into cannabinoids like CBN and THCV have also hinted at benefits ranging from aiding sleep to regulating blood sugar levels, signifying a rich scope for medicinal use.
As the scientific community delves into the complexities of these compounds, the future of cannabinoid research holds promising advancements that could redefine their role in therapeutic settings.
The depth of this botanical class harbors vast potential for new discoveries, enhancing understanding of not only individual cannabinoid effects but also their interactions and synergies within the human endocannabinoid system. With a growing body of evidence, cannabinoids may soon provide a framework for novel treatments, expanding the boundaries of current medical practice.
Understanding Cannabinoids
The study of cannabinoids reveals a complex interplay with the endocannabinoid system, key in maintaining homeostasis in the body. This section dissects the fundamental aspects of cannabinoids, their interaction with the ECS, and specifically the crucial CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Cannabinoid Basics
Cannabinoids are a class of diverse chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant. They act on cannabinoid receptors in cells that alter neurotransmitter release in the brain. To date, over 100 different cannabinoids have been identified, with THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) being the most well-known.
Other notable cannabinoids include CBN (cannabinol), CBC (cannabichromene), CBG (cannabigerol), and THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin), each with distinct effects and potential therapeutic applications.
Common Cannabinoids:
- THC: Psychoactive, pain relief
- CBD: Non-psychoactive, anti-inflammatory, anxiety relief
- CBN: Mild psychoactivity, sedative
- CBG: Antibacterial, neuroprotective
- CBC: Anti-inflammatory, analgesic
- THCV: Appetite suppressant, regulates blood sugar
The Endocannabinoid System
The study of cannabinoids reveals a complex interplay with the endocannabinoid system, key in maintaining homeostasis in the body. This section dissects the fundamental aspects of cannabinoids, their interaction with the ECS, and specifically the crucial CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Cannabinoid Basics
Cannabinoids are a class of diverse chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant. They act on cannabinoid receptors in cells that alter neurotransmitter release in the brain.
To date, over 100 different cannabinoids have been identified, with THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) being the most well-known. Other notable cannabinoids include CBN (cannabinol), CBC (cannabichromene), CBG (cannabigerol), and THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin), each with distinct effects and potential therapeutic applications.
Common Cannabinoids:
- THC: Psychoactive, pain relief
- CBD: Non-psychoactive, anti-inflammatory, anxiety relief
- CBN: Mild psychoactivity, sedative
- CBG: Antibacterial, neuroprotective
- CBC: Anti-inflammatory, analgesic
- THCV: Appetite suppressant, regulates blood sugar
The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the early 1990s through the research on THC. It plays a crucial role in regulating a range of functions and processes, including mood, memory, appetite, pain, sleep, and maintaining cellular balance or homeostasis.
The ECS comprises endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes. Endocannabinoids, such as anandamide, are molecules produced by the body that bind to cannabinoid receptors.
Cannabinoid Receptors: CB1 and CB2
The ECS functions through two primary cannabinoid receptors: CB1 and CB2. These receptors are found throughout the body, with CB1 receptors primarily located in the brain and nervous system and CB2 receptors more widespread but particularly present in the immune and gastrointestinal systems.
- CB1 Receptors:
- Located in: Brain, spinal cord
- Functions: Modulate mood, memory, sleep, appetite
- THC Binding: Causes psychoactive effects
- CB2 Receptors:
- Located in: Immune cells, peripheral organs
- Functions: Anti-inflammatory effects, immune response
- CBD Interaction: Influences reduction of inflammation without psychoactive effects
Major Cannabinoids
The two primary cannabinoids that have been extensively researched and are well-known for their effects on the human body are THC and CBD. They serve distinct purposes and have different impacts on health and the sensation of a ‘high.’
THC: Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol, more commonly referred to as THC, is the primary psychoactive component of the cannabis plant. It is responsible for the ‘high’ that is often associated with cannabis use.
The effects of THC include a sense of euphoria, relaxation, and altered sensory perception. However, THC is not solely about its psychoactive properties; it has also been recognized for its potential in medical use. It may offer pain relief and has been suggested to have neuroprotective properties.
| Aspect of THC | Description |
|---|---|
| Psychoactive Effects | Induces a ‘high’, impacting mood and cognition. |
| Health Applications | Used for pain relief and may have neuroprotective benefits. |
| Impact on the Body | Affects the endocannabinoid system, leading to various physiological responses. |
CBD: Cannabidiol
Cannabidiol, or CBD, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, meaning it does not cause a ‘high.’ It is renowned for its health benefits, providing relief from inflammation and pain without the psychoactive effects of THC. CBD has been studied for its potential medical uses, and it is considered to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. A significant aspect of CBD is its role in the entourage effect, where it is believed to work synergistically with other cannabinoids, enhancing their overall therapeutic potential.
| Aspect of CBD | Description |
|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | Lacks the intoxicating effects commonly associated with THC. |
| Health Applications | May relieve inflammation, pain, and has neuroprotective potential. |
| Entourage Effect | May enhance the efficacy of other cannabinoids when combined. |
Minor Cannabinoids and Their Effects
As research into cannabis compounds expands beyond the well-known THC and CBD, a range of minor cannabinoids emerges with distinct effects and potential benefits. These lesser-known cannabinoids contribute to the entourage effect and offer varied interactions with the human body’s endocannabinoid system.
CBN: Cannabinol
Cannabinol (CBN) is a non-psychoactive compound known to have sedative properties. It arises from the degradation of THC and is often touted for its potential to help with sleep.
CBG: Cannabigerol
Cannabigerol (CBG) is found in lower concentrations in the cannabis plant. It’s recognized for its anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and neuroprotective benefits. Like CBN, CBG is non-psychoactive and may affect the brain without intoxication.
THCV: Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is similar in structure to THC but with distinct properties. It can act as an appetite suppressant, which is the opposite of the usual appetite stimulant quality of THC, and may support mood regulation.
THCP: Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Currently, THCP (tetrahydrocannabiphorol) information is limited and often confused with THCV due to a similarity in names. Where accurately described, THCP has been found in minute concentrations and might interact with the endocannabinoid system more potently than THC, but its effects are still under investigation.
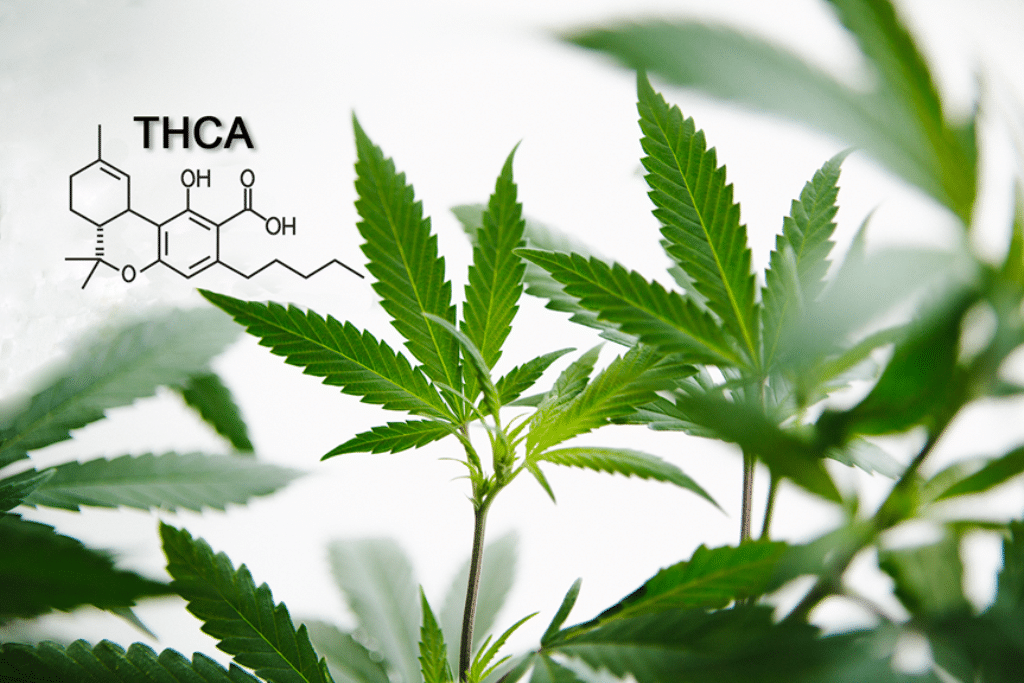
THCA: Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is a non-psychoactive precursor to THC found in the raw cannabis plant. THCA may hold anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, which become active once decarboxylated into THC.
CBC: Cannabichromene
Cannabichromene (CBC) is another non-psychoactive cannabinoid with notable anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. Along with others, CBC contributes to the overall therapeutic profile of cannabis in its interaction with the brain and potential influence on mood.
Minor Cannabinoid Brands
The cannabis industry has seen an expansion with brands focusing on minor cannabinoids. These companies are innovating beyond THC and CBD, offering products rich in compounds like CBN, CBG, and THCV.
Space Gods
Space Gods has established itself as a brand that offers an array of cannabinoid-infused products. They uniquely cater to niche markets seeking the benefits of rarer cannabinoids. Customers typically choose Space Gods Delta 9 products for their quality-controlled manufacturing process which ensures high purity and potency of CBN and CBG in their edibles and tinctures.
Delta Munchies
Delta Munchies is recognized for their flavorful and potent cannabinoid-infused snacks. Their product line is diverse, extending from gummies to baked goods. Two standout features of Delta Munchies are:
- Product Variety: A vast selection of snacks, each infused with different minor cannabinoids, providing customers with multiple consumption options.
- Focused Effects: Products are tailored for specific results, such as relaxation or pain relief, leveraging the unique properties of minor cannabinoids.
3Chi
3Chi is a pioneer brand at the forefront of minor cannabinoid products, noted for their scientific approach to extraction and product formulation. They offer a comprehensive selection of cartridges, oils, and edibles. Highlights of 3Chi include:
- Innovative Extracts: Expertise in extracting pure CBG, CBN, and THCV.
- Educational Resources: Commitment to educating consumers about the benefits and science behind minor cannabinoids.
Minor Cannabinoids and Their Effects
Exploring minor cannabinoids reveals a complex landscape beyond THC and CBD, each with unique properties affecting the body’s endocannabinoid system. These compounds show promise in therapeutic applications, displaying a variety of effects from sedative to anti-inflammatory.
CBN: Cannabinol
Cannabinol (CBN) is known for its sedative qualities. Research suggests that CBN may act as a potent sedative when combined with THC, and could be beneficial in treating sleep disorders due to its tranquilizing effects.
THCP: Tetrahydrocannabiphorol
Tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) is a minor cannabinoid structurally similar to THC but with a crucial difference: it has a longer alkyl side chain, allowing it to bind more effectively to CB1 receptors in the brain. This enhanced binding potentially makes THCP much more potent than THC, leading to stronger psychoactive effects.
THCP vape products have emerged, offering users a new way to experience its heightened potency. These products deliver THCP in a concentrated form, providing a convenient consumption method. However, due to its increased potency, caution is advised when using THCP vapes, with recommendations to start with lower doses.
The full effects, therapeutic benefits, and safety profile of THCP are still being studied, making it important for users to approach these products with awareness of their potent nature.
CBG: Cannabigerol
Cannabigerol (CBG) is often referred to as the “mother of all cannabinoids” as it is the precursor from which other cannabinoids are synthesized. It is non-psychoactive and has been studied for its potential antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it a subject of significant interest in medical research.
THCV: Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is similar to THC, but with different effects. It is reported to act as an appetite suppressant, which could make it useful in weight management. Additionally, THCV may also help in regulating blood sugar levels and reducing insulin resistance.
CBC: Cannabichromene
Cannabichromene (CBC) is another non-intoxicating cannabinoid that has garnered attention for its potential anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. It could also play a role in the body’s natural response to inflammation and has been associated with mood elevation.
Emerging Research and New Discoveries
Recent scientific endeavors have expanded the spectrum of known cannabinoids, moving beyond the familiar THC and CBD. These advancements have set the stage for a deeper understanding of cannabis science, with a particular focus on new cannabinoids and their journey through clinical trials.
Exploring New Cannabinoids
Researchers are venturing into uncharted territories of the cannabis plant, identifying compounds like CBG (cannabigerol), CBN (cannabinol), and THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin). These substances present unique effects and potential therapeutic properties. For example, CBG has been observed to exhibit anti-inflammatory qualities, while CBN is being studied for its sedative effects, which could aid sleep. Similarly, THCV shows promise in regulating blood sugar levels.
Cannabis research blogs play a vital role in disseminating information on these findings, making complex data more accessible to both the scientific community and the public. Through meticulous analysis and reporting, the contributions of these new cannabinoids are beginning to be recognized.
Cannabinoids in Clinical Trials
The journey from discovery to application involves stringent clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy. Presently, various clinical studies are exploring how these new cannabinoids can be effectively integrated into treatment protocols. For instance, a Canadian clinical trial observed the effectiveness of CBD-rich treatments on symptoms such as pain, anxiety, and depression.
Although still in the early stages, this research holds significant promise for the future of medical cannabis and its potential to offer novel therapeutic avenues. Each trial contributes valuable insights, paving the way for approved medical applications of these emerging compounds.
Cannabinoids and Consumables
Exploring the world of cannabinoids goes beyond THC and CBD, extending to consumables that showcase the versatility and potential therapeutic uses of lesser-known cannabinoids. Consumers now have a variety of cannabinoid-infused options for both recreation and wellness purposes.
Edibles and Infusions
Cannabinoid edibles and infusions have diversified with the emergence of rare cannabinoids like CBN, CBC, and CBG. These consumables, which include gummies, chocolates, and beverages, are sought after for their potential non-intoxicating therapeutic benefits. The Farm Bill’s legalization of hemp derivatives has expanded product safety and legality, leading to a novel array of edibles that promise well-being without the psychoactive effects typically associated with THC.
- Types of Edible Products:
- Gummies
- Chocolate bars
- Infused drinks
- Targeted Effects:
- Sleep aid (commonly associated with CBN)
- Anti-inflammatory (linked with CBC and CBG)
Vaping and Smoking Alternatives
Vaping products containing rare cannabinoids offer alternatives to traditional smoking, delivering cannabinoids in a method that many consumers find more appealing. Additionally, the innovation within vaping technology aligns with a growing demand for recreational experiences that do not necessarily involve intoxication. It is paramount, however, that products adhere to stringent safety standards to prevent health risks often associated with illicit market vape products.
- Vaporizable Forms:
- Pre-filled vape cartridges
- Disposable pens
- Concentrates for dabbing
- Notable Points:
- Vaping provides rapid onset of effects
- Product safety is crucial, emphasizing the need for proper labeling and third-party testing