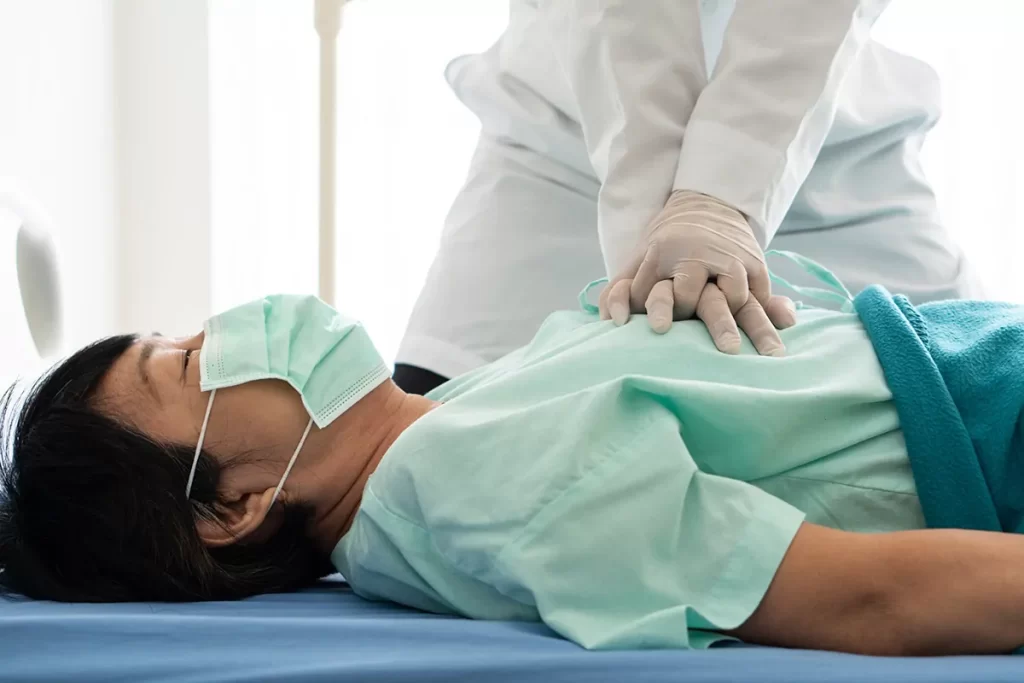
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is a vital life-saving method that plays a critical role in emergency scenarios where an individual’s heart has ceased functioning or they have ceased to breathe.
It involves a series of actions aimed at restoring the flow of oxygenated blood to the brain and vital organs, increasing the chances of survival until professional medical help arrives. In this article, we will explore the importance of BLS/CPR, its main techniques, and its impact on saving lives.
Components of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
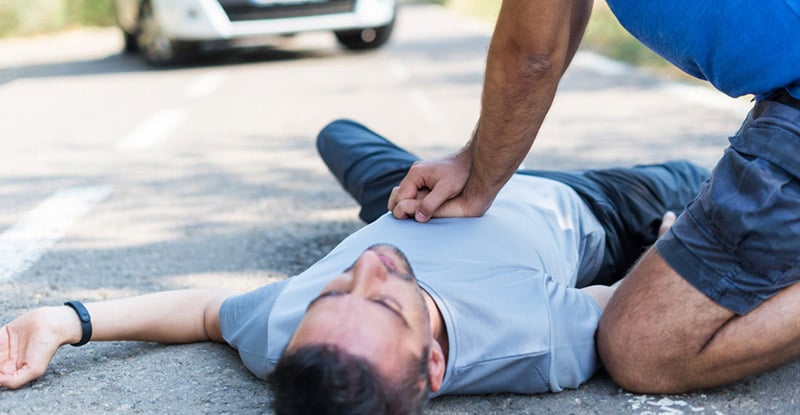
- Chest compressions: Applying pressure to the center of the individual’s chest using the palm of your hand is a crucial part of performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). The objective is to exert firm downward force, reaching a depth of at least 2 inches (5 centimeters) and maintaining a rhythm of 100-120 compressions per minute. These compressions serve the purpose of manually stimulating the heart, facilitating the circulation of blood to critical organs.
- Rescue breaths: Rescue breaths, also known as mouth-to-mouth ventilation, involve providing breaths to the victim to restore oxygen exchange in the lungs. Following 30 chest compressions, incline the individual’s head slightly backward and elevate their chin to unblock the air passage. Seal the victim’s nostrils by pinching them together, cover their mouth with yours, and administer two gentle breaths. Each breath should endure approximately one second and result in noticeable expansion of the chest..
- Airway management: Ensuring an open airway is essential during CPR. Before delivering rescue breaths, check for any obstructions such as foreign objects, vomit, or the victim’s tongue blocking the airway. If an obstruction is present, gently remove it using your fingers or by tilting the head back and sweeping the mouth with your fingers.
- Early defibrillation: If there is access to an automated external defibrillator (AED), it is crucial to utilize it promptly. AEDs administer an electrical impulse to the heart, reinstating its regular rhythm when encountering cardiac arrest due to specific forms of arrhythmias. Follow the AEDs voice prompts and adhere to the recommended steps for safe and effective defibrillation.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation for Special Populations
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation for Special Populations refers to adaptations and modifications in cardiopulmonary resuscitation techniques to cater to individuals with specific needs or conditions. Here is an enumeration and explanation of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation For various special populations:
- Persons with Disabilities: A program has been developed to empower people with disabilities to advise others on performing Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and using automated external defibrillators (AEDs). This program aims to ensure that individuals with disabilities can actively contribute to saving lives in emergency situations.
- Pregnant Individuals: When performing Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation on a pregnant person, the technique remains similar to standard Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. However, the rescuer should position their hands slightly higher on the chest to avoid pressure on the abdomen. It is essential to ensure continuous high-quality chest compressions and appropriate airway management.
- Obese Individuals: For individuals with obesity, the rescuer may need to use more force during chest compressions due to the increased body mass. Maintaining a proper hand placement and depth of compressions is crucial to provide effective circulation.
- Patients with Comorbidities: Particular attention must be given when administering Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation to individuals with significant concurrent medical conditions, such as asthma or heart failure with ventricular assist devices. Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation guidelines specific to these conditions should be followed to maximize the chances of successful resuscitation.
- Children with Special Needs: Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation techniques for children with special needs do not differ significantly from standard Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. However, it is essential to adapt the approach based on the child’s individual condition and needs. Caregivers and medical professionals need to be trained to provide CPR and first aid to children with special needs effectively.
- Underserved Populations: Bystander Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation occurs less frequently in underserved communities, leading to lower survival rates. Efforts have been made to provide CPR training specifically targeted towards underserved populations to increase their knowledge and ability to respond during emergencies.
Adapting Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Techniques for special populations emphasizes the importance of inclusivity and ensuring that everyone, regardless of their physical or medical condition, receives the necessary care during cardiac emergencies. Proper training and certification programs specific to these populations have been developed to equip individuals with the skills needed to provide effective Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation.
Components of Post-Cardiac CPR Arrest Care
Post-cardiac arrest care refers to the comprehensive medical treatment and interventions provided to individuals who have experienced a cardiac arrest and successfully regained spontaneous circulation.
- Immediate assessment and stabilization: After successful resuscitation, the individual’s vital signs, level of consciousness, and oxygenation are closely monitored. Any ongoing interventions, such as mechanical ventilation or medication administration, are continued or adjusted as necessary.
- Targeted temperature management (TTM): TTM, also known as therapeutic hypothermia or targeted hypothermia, is a key component of post-cardiac arrest care. It involves lowering the patient’s body temperature to a specific target range (usually around 32-36°C or 89.6-96.8°F) for a defined period (usually 24-48 hours). TTM has been shown to improve neurological outcomes and decrease brain damage following cardiac arrest.
- Coronary angiography and revascularization: When cardiac arrest is a result of a heart attack due to blocked coronary arteries, doctors may conduct coronary angiography to assess the extent of artery disease. If significant blockages are identified, procedures like percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) can be performed to restore blood flow and decrease the chances of future cardiac incidents.
- Hemodynamic optimization: The patient’s hemodynamic stability is carefully managed to optimize cardiac function and perfusion. To bolster blood pressure and cardiac output, medicines such as vasoconstrictors or positive inotropic agents may be given. Fluid resuscitation is guided by careful monitoring of central venous pressure, arterial blood pressure, and other parameters.
- Oxygenation and respiratory support: Adequate oxygenation and ventilation are crucial during post-cardiac arrest care. Mechanical ventilation may be continued or adjusted as needed to maintain appropriate oxygen levels and respiratory function. Blood gasses and other parameters are closely monitored to guide treatment.
- Neurological monitoring and management: Continuous neurological monitoring is performed to assess brain function and detect any signs of neurologic injury. Additional interventions, such as seizure prophylaxis or treatment, may be initiated if necessary. Neurological assessments, including neuroimaging studies, may also be conducted to evaluate brain damage or other abnormalities.
- Supportive care and rehabilitation: Providing emotional assistance, psychosocial interventions, and engaging families are crucial elements of post-cardiac arrest treatment. Rehabilitation, which encompasses physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, may be initiated to facilitate functional recuperation and enhance long-term results.
⚠ Article Disclaimer
The above article is sponsored content any opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and not necessarily reflect the views of CTN News