Learning
How Does An Induction Furnace Work?
Induction furnaces have been integral in the manufacturing industry for decades. These furnaces are known for their efficiency and speed in melting metals and alloys.
They have become a popular choice for industries that require high-temperature melting of metals. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at the science behind how an induction furnace works.
We will explore the different components of an induction furnace and how they work together to create a precise and controlled melting process. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of induction furnaces.
What is an induction hob?
If you are looking for a new hob for your kitchen, you might have come across the term “induction hob”. But what exactly is an induction hob, and how does it work?
Put simply, an induction hob is a type of cooktop that uses electromagnetic energy to heat your cookware directly, instead of heating the surface of the hob itself. This makes it more efficient, faster, and safer than traditional gas or electric hobs.
To understand how induction hobs work, let’s take a closer look at their key features and benefits.
How do induction hobs work?
Induction hobs are made up of a flat, glass-ceramic surface with an electromagnetic coil underneath. When you turn on the hob and place a magnetic pan on the surface, the coil generates a magnetic field that creates an electric current inside the pan. This current generates heat, which then cooks the food directly.
Because the heat is generated inside the pan, induction hobs are more precise and controllable than traditional hobs. You can easily adjust the heat levels with a touch of a button, and the heat will respond almost instantly to your changes.
What are the benefits of an induction hob?
There are several benefits to using an induction hob over a traditional hob:
1. Efficiency: Induction hobs are more energy-efficient than gas or electric hobs, as they only heat the cookware and not the hob surface. This means that less heat is wasted and your food will cook faster.
2. Safety: Induction hobs are safer to use than gas or electric hobs, as the surface remains cool to the touch and there is no open flame. This makes them ideal for households with children or pets.
3. Easy to clean: The flat surface of an induction hob is easy to clean and maintain, as there are no burners or grates to remove. Simply wipe the surface with a damp cloth to remove any spills or stains.
4. Precise temperature control: Induction hobs offer precise temperature control, making it easy to cook delicate dishes or achieve the perfect sear on a steak.
5. Stylish design: Induction hobs have a sleek and modern design that will complement any kitchen. They are available in a range of sizes and styles to suit your cooking needs.
Types of induction furnaces
1. Coreless Induction Furnace
The coreless industrial induction furnace is the most popular induction furnace type. It is designed to melt non-ferrous metals such as copper, aluminum, and precious metals.
The furnace consists of an external shell made of steel and an inner lining of refractory material. Inside the furnace, there is a coil that generates an alternating magnetic field that induces eddy currents in the metal charge causing it to heat and melt.
The coreless induction furnace is highly efficient and can melt metal quickly, which makes it ideal for high-volume production. It is also easy to operate and maintain, making it a popular choice in foundries and other industrial settings.
2. Channel Induction Furnace
The channel induction furnace is designed to melt ferrous metals such as steel and cast iron. It has a U-shaped channel that acts as a crucible to hold the metal charge. The channel is made of refractory material and is surrounded by a coil that generates an alternating magnetic field.
The channel induction furnace is highly efficient, with low energy consumption and minimal heat loss. It is also versatile, as it can melt a wide range of ferrous metals. The furnace is commonly used in steel mills, foundries, and other industrial settings.
3. Crucible Induction Furnace
The crucible induction furnace is designed to melt small batches of metal, typically less than 500 kg. It consists of a crucible made of refractory material and a coil that generates an alternating magnetic field. The crucible is heated by the magnetic field, which induces eddy currents in the metal charge, causing it to heat and melt.
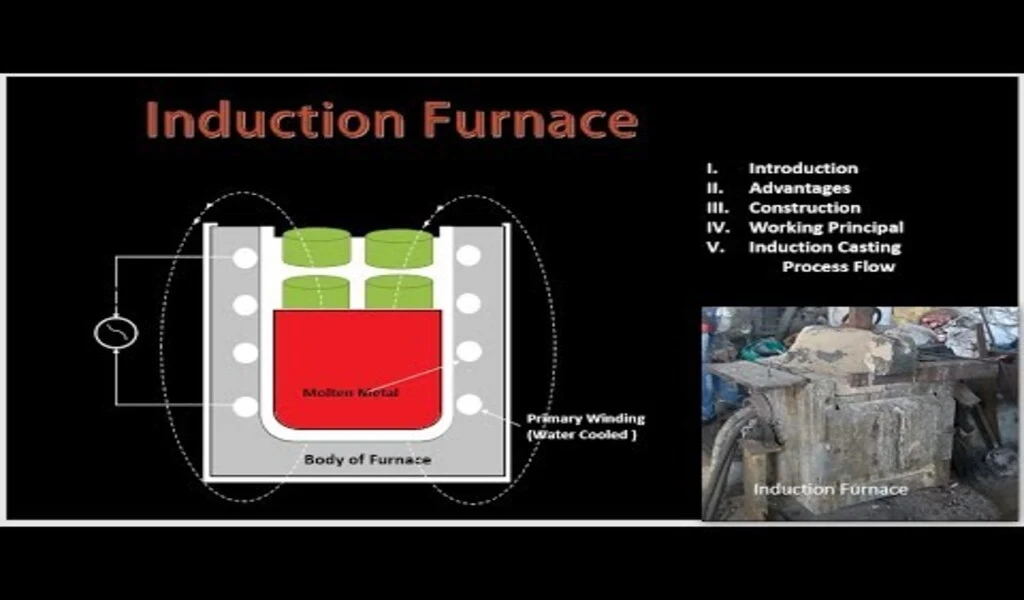
Working principle of induction furnace
Induction furnaces work by generating an electromagnetic field that induces an electric current in a conductive material, such as metal.
The furnace consists of an alternating current (AC) source that supplies power to a coil made of copper or another conductive material. When an AC current flows through the coil, a rapidly changing magnetic field is created around it.
When a conductive material, such as metal, is placed inside the coil, the rapidly changing magnetic field induces an electric current in the metal.
This electric current generates heat, which melts the metal. The heat generated is directly proportional to the amount of current induced in the metal and the electrical resistance of the metal.
Induction furnaces can be operated using two different frequency ranges – low frequency (50-60 Hz) and high frequency (100 kHz-2 MHz).
Low-frequency induction furnaces are primarily used for melting iron and steel, while high-frequency induction furnaces are used for melting non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, copper, and brass.
What Kind of Metal Can be Melted by Induction Furnace?
Induction furnaces can melt a wide range of metals, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Ferrous metals, such as iron and steel, are the most commonly melted metals using induction furnaces. Non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, copper, brass, and nickel, can also be melted using induction furnaces.
The melting capacity of an induction furnace depends on several factors, including the frequency of operation, the size of the furnace, and the type of metal being melted. High-frequency induction furnaces have higher melting capacities compared to low-frequency induction furnaces.
Induction furnaces are widely used in the manufacturing industry for melting and processing metals. They offer several advantages, including energy efficiency, lower emissions, and faster melting times.
Additionally, induction furnaces have a higher degree of process control, which allows for better quality control during the melting process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the working principle of induction furnace is based on the principles of electromagnetic induction, which involves the creation of an electric current in a conductor by varying the magnetic field around it.
Induction furnaces can melt a wide range of metals, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals. They offer several advantages over traditional melting methods and are widely used in the manufacturing industry.
SEE ALSO: Memorial Day 2023: Honoring The Sacrifices And Celebrating The Spirit Of Patriotism