Learning
Mad Honey Explores Sustainability of Harvesting Organic Bee Honey

Mad Honey, with its distinctive psychoactive properties, has gained both fame and infamy. Its increasing popularity has brought attention to several ethical concerns, including bee conservation, exploitation, and sustainability. This piece will explore these aspects, outlining the moral considerations that surround Mad Honey.
The ethical debate surrounding Mad Honey is multifaceted, encompassing concerns about conservation, exploitation, sustainability, and responsible consumption. As interest in this unique honey grows, so does the responsibility to approach it with ethical consideration and care.
From protecting natural habitats and respecting indigenous cultures to ensuring sustainable practices and legal compliance, the path to enjoying Mad Honey responsibly is complex but attainable. Collaboration between beekeepers, communities, regulators, and consumers is vital to honoring the rich heritage of Mad Honey while safeguarding its future for generations to come.
Conservation of Natural Habitats
Challenges:
Over harvesting: The increasing demand for Mad Honey might lead to over harvesting, potentially harming the wild bee populations that produce it.
Habitat Destruction: Expansion of Mad Honey production could lead to destruction or alteration of natural habitats, affecting the rhododendron plants and the bees.
Solutions:
Protected Areas: Designating specific regions for the conservation of wild bee populations and rhododendron plants.
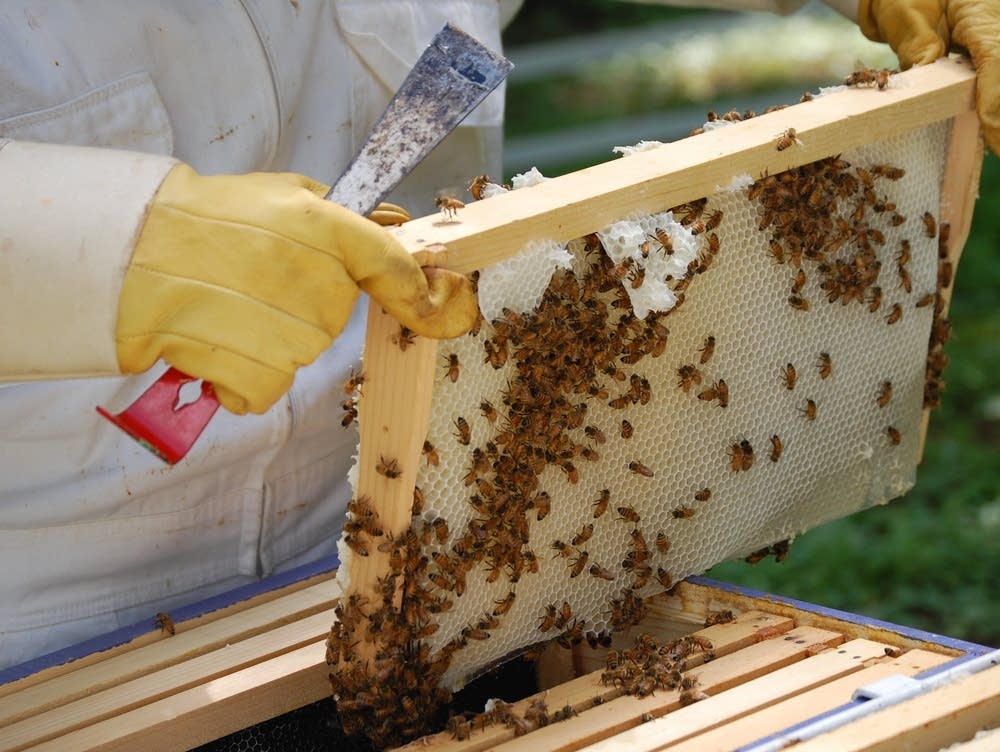
Responsible Harvesting: Implementing guidelines for ethical harvesting, ensuring the survival of bee colonies.
Exploitation of Indigenous Communities
Challenges:
Loss of Traditional Knowledge: The commercialization of Mad Honey may lead to a loss of traditional harvesting techniques and cultural heritage.
Economic Exploitation: Indigenous communities may not receive fair compensation for their knowledge and labor in Mad Honey production.
Solutions:
Fair Trade Practices: Ensuring fair compensation and recognizing the rights and contributions of indigenous communities.
Cultural Preservation: Supporting and preserving traditional practices and knowledge associated with Mad Honey.
Sustainability of Mad Honey Production and Harvesting
Challenges:
Unsustainable Harvesting: Without careful management, Mad Honey harvesting can become environmentally unsustainable.
Quality Control: The increased demand might lead to the dilution of authentic Mad Honey, impacting quality and safety.
Solutions:
Sustainable Practices: Encouraging beekeepers to adopt sustainable practices that ensure the continued availability of Mad Honey.
Quality Assurance: Implementing stringent quality control measures to maintain the integrity of Mad Honey.
Legal and Ethical Consumption
Challenges:
Illegal Trade: In some regions, the sale and consumption of Mad Honey might be restricted or illegal.
Uninformed Use: Consumers might be unaware of the potential risks and proper dosages of Mad Honey.
Solutions:
Legal Compliance: Ensuring that Mad Honey is produced, sold, and consumed within legal frameworks. Make sure to buy Mad honey from a ethical source.
Education and Awareness: Educating consumers about the safe and responsible use of Mad Honey.